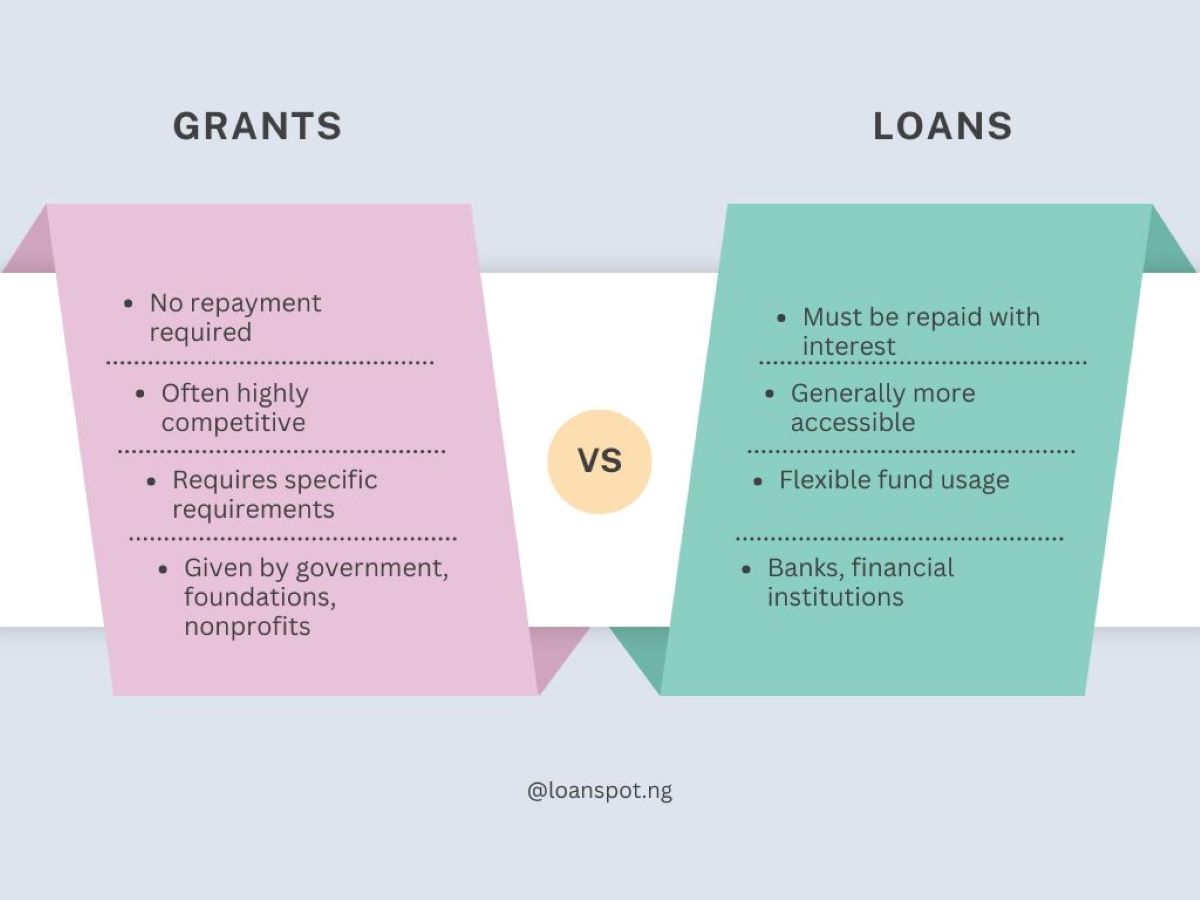
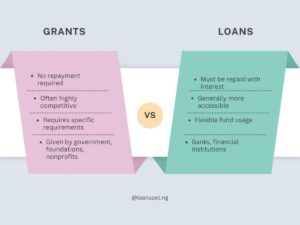
There are several debt instruments i.e assets that require a fixed payment to the holder, usually with interest (such as bonds and mortgages ) available in the commercial market.
However, when in need of capital, most companies use debentures (which is a type of bond) to borrow money either for expansion or other business developments.

What are Debentures?
The word “Debenture” is from the Latin word “Debentur” which means “to owe”. It recognizes debentures as one of the major debt instruments in the commercial community.
It is a type of bond used by companies and the government to issue a loan at a fixed rate of interest. Debentures are usually long-term security and they secure it on assets.
In simpler terms, a debenture is a document a company issues as an acknowledgement, at one point or the other, and for specific purposes, borrow a certain amount of money from the public.
Significance of a debenture certificate
This document also signifies the company’s promise to repay under some terms or at a specific future date. Therefore, Debenture holders can be referred to as creditors of such a company.
What are the types of Debentures?
There are several types of Debentures, they include
Secured and Unsecured:
A debenture is referred to as secured when the debt security is in an asset or set of an asset. They can also call this a mortgage debenture and they often put the assets in question in the care of a trustee.
A debenture is insecure or naked when the agreement is solely upon the credibility of the issuer.
Registered and Bearer:
When a company registers a debenture, it means the issuing company has recorded certain details such as name, address, and other holding details.
They must update this record whenever they transfer the debenture to another holder. This is quite important as the issuing company only pays to a registered holder.
An unregistered however is a bearer debenture where transfer procedures come easy such that they can make it to a new holder by mere delivery. Here, whoever produces the coupons attached to the debenture certificate gets paid.
Convertible and Non-Convertible:
When a debenture is convertible, it means the holder gets to convert his holdings into equity shares. However, information as to the time and rate of such conversion must have been clearly stated in the terms of the debentures agreement as at the time they issued it.
As opposed to this, non-convertible debentures do not provide for conversion. It is a simple debenture that cannot go beyond the original purpose of a debenture which is debt.
First and Second:
This is an extension of the Secured / Mortgaged debentures.
It must fulfil two major obligations on the assets obtained as security, respectively.
It refers the primary and first charge over the asset to as first mortgaged debentures while they know the second charge as the second mortgaged debentures
Redeemable and Irredeemable:
A company regards a debenture as Redeemable where a specific date has been fixed on the debenture certificate for redemption. This puts the issuing company under a compulsory obligation to repay the principal amount to the debenture holder on the date assigned.
Irredeemable debentures or perpetual debentures are a direct opposite, there is no record for a redemption date. Redemption here is usually either done on the company’s liquidation or according to other terms of the agreement between the company and the holder.
How does Debentures work?
Ultimately, a debenture doesn’t work like a strictly configured standard product.
Established on the agreement made between a company and the debenture holder. They both decide the terms and conditions to follow in the debenture agreement.
Debentures are like traditional bonds with the only difference being the fact that debentures do not require collateral. They usually buy Debenture bonds on the assumption that the company borrowing will repay.
However, if the company runs bankrupt or goes out of business, its assets will be liquidated, and they make an order to pay all its potential lenders.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Debentures
The following are the salient advantages of debentures:
- It provides investors with fixed income and interest rates at lesser risk.
- A company can issue Debentures without having to give up the control of its equitable shareholders.
- The interest payment on debentures is tax-deductible.
- Sourcing for finance through debentures is less costly as compared to other debt instruments.
- Debentures do not cover/affection a company’s profits.
Disadvantages
- It reduces a company’s borrowing capacity.
- Where under a redeemable debenture, it legally binds a company to comply with the assigned date irrespective of its financial strength at that time.
- Debenture puts a company at risk during market fluctuations because it places a permanent burden on its earnings.
Conclusion
To secure the future of any company, capital is a necessity and it is best to venture into business expansion or projects using debentures in situations where your company’s sales, profits, and earnings are stable.
Check out the Related Posts below:
- Loan amortization – Meaning, types, and how it works
- Peer to Peer lending in Nigeria and how it works
- Targeted Credit Facility - Meaning and how to apply
- Loan Liquidation Meaning & How to Liquidate Your Loan
- Branch Loan: A Review and How to Get A Loan From Branch
- UBA Loan - Requirements and How to Apply for Loans from UB